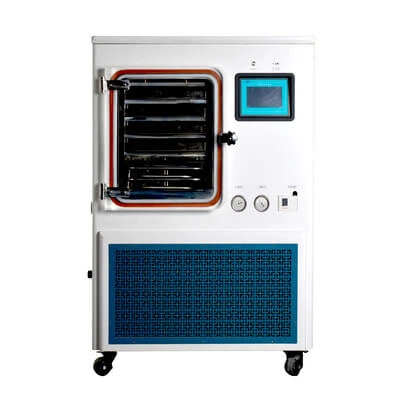
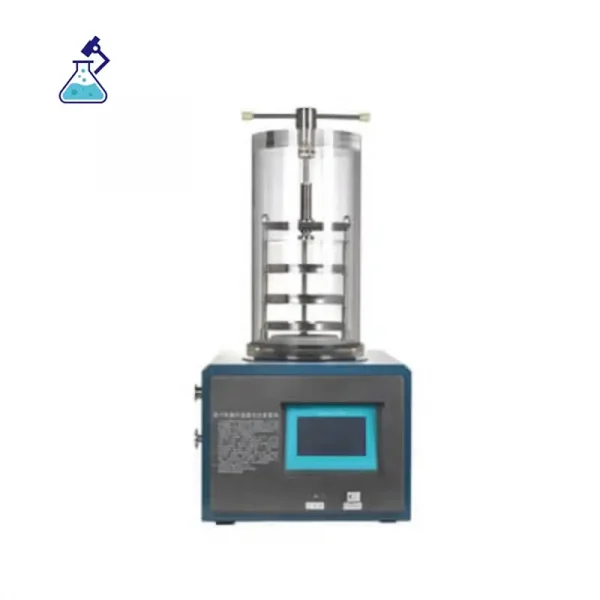
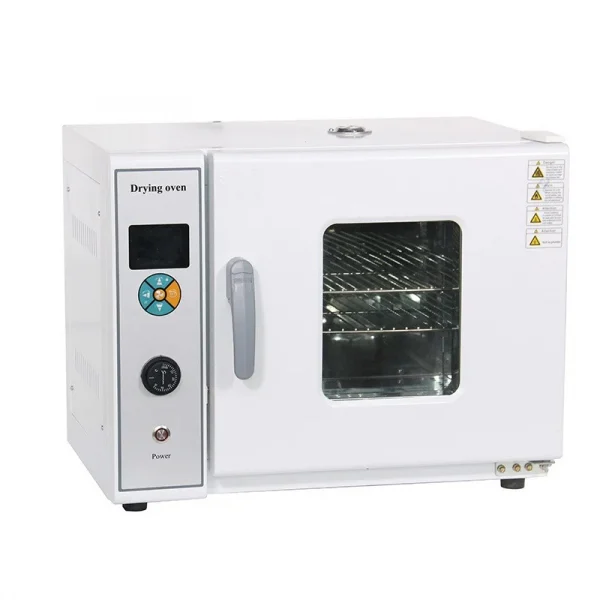
Description
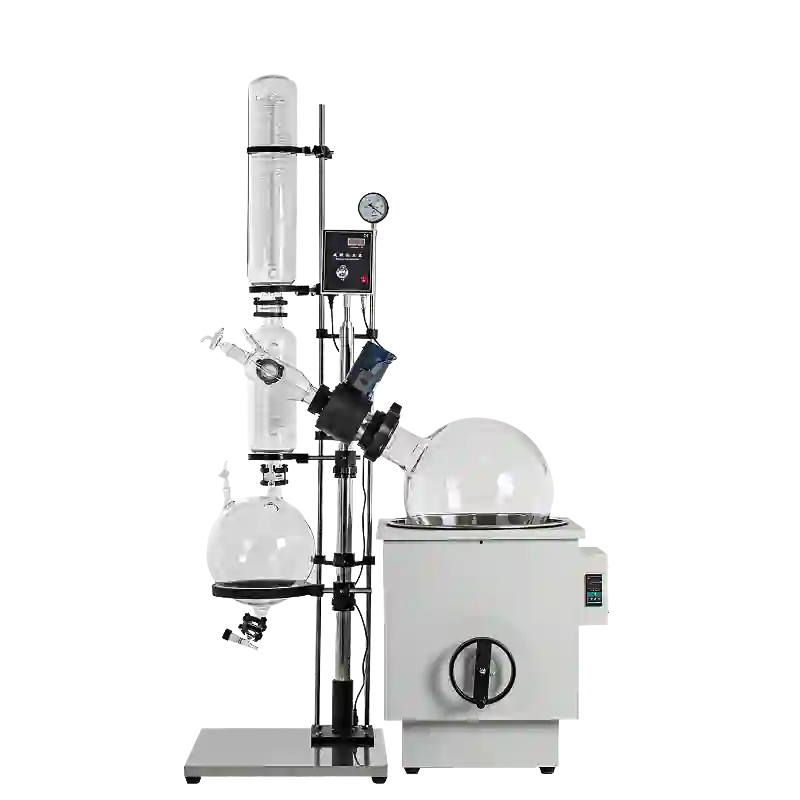
Labonsale’s Rotary Evaporator, also known as rotovap, rotavapor, or rotary vacuum evaporator, is a pinnacle of precision and efficiency in solvent evaporation. Tailored for a range of applications such as distillation, concentration, and drying, our rotary evaporator incorporates cutting-edge technology to meet the diverse needs of laboratories and industries.
We offer a variety of options, including:
- Manual/Electric Lift Rotary Evaporator
- Ex-Proof upgrade Rotary Evaporator
- Dual Condenser & Dual Reflex rotary evaporators
- Customized services
For more information or to inquire about our rotary evaporator price range, please contact us, we have rotary evaporator for sale.
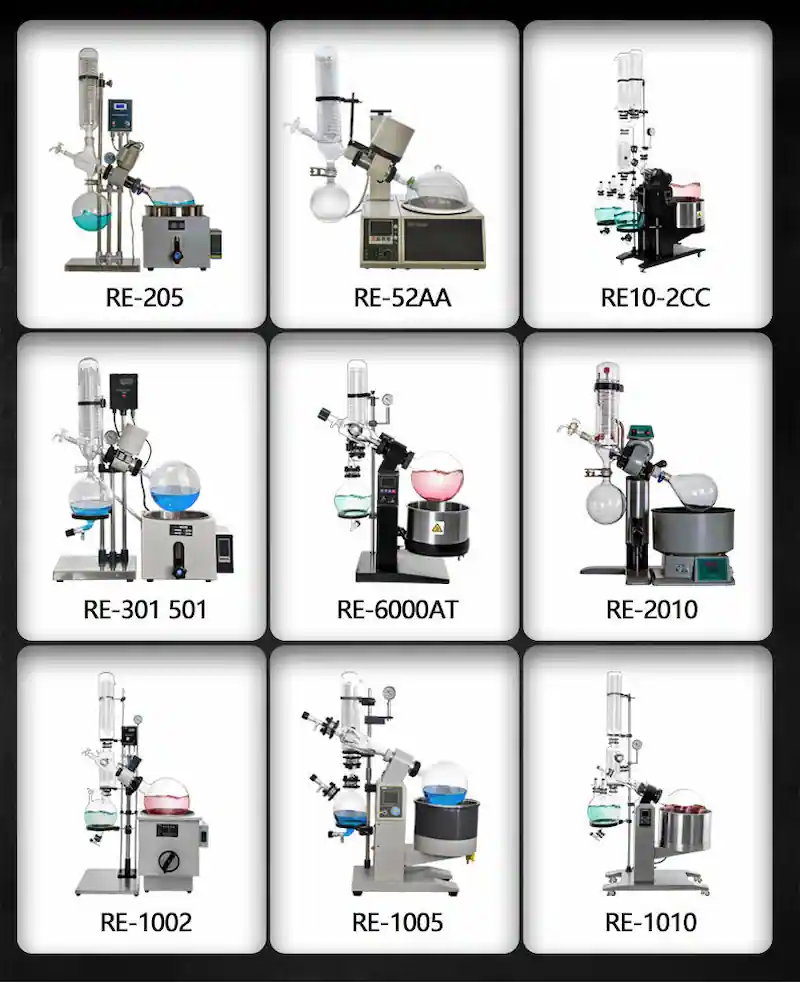

Technical Parameter of Rotary Evaporator
| Model | RE-205 | RE-52AA | RE-2010 | RE-301 | RE-501 | RE-6000AT |
| Photo | 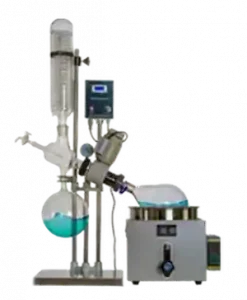 |  |  |  |  |  |
| Condenser | Vertical Double Serpentine Coils | |||||
| Lifting mode | Manual | Electric | Gravity Balance | Manual | Electric | |
| Evaporation Ability | 20ml/min | 25ml/min | 40ml/min | 50ml/min | ||
| Condensation area(㎡) | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | ||
| Rotation Speed | 0~180rpm | 0~120rpm | 0~150rpm | |||
| Vacuum Degree | -0.095Mpa | |||||
| Evaporating Speed (H2O) | >1.2L/h | >2L/h | >3L/h | |||
| Temperature Range | Water Bath:RT~99℃ , Oil Bath:RT~200℃ | |||||
| Heating Power | 1.5KW | 2KW | ||||
| Motor Power | 40W | 60W | ||||
| Display | LCD Digital display for rotation speed and heating temperature | |||||
| Rotary Flask | 0.5~ 2L | 3L | 5L | 6L | ||
| Collection Flask | 1L φ35mm (Ball Joint) | 2L Bottom Valve | 3L Bottom Valve | |||
| Vacuum & Sealing | Teflon + Teflon fluorinated rubber double seal | |||||
| Bath Dimensions | φ240mm*150H | φ260mm*150H | φ280mm*150H | φ300mm*170H | ||
| Lift Distance | 0~150mm | 0~180mm | ||||
| Voltage/Frequency | 220V/ 50-60HZ(Optional 110V) | |||||
| Dimension(L*W*H) | 63*33*106cm | 54*45*73cm | 49*36*73cm | 69*35*110cm | 73*40*115cm |
Product Details
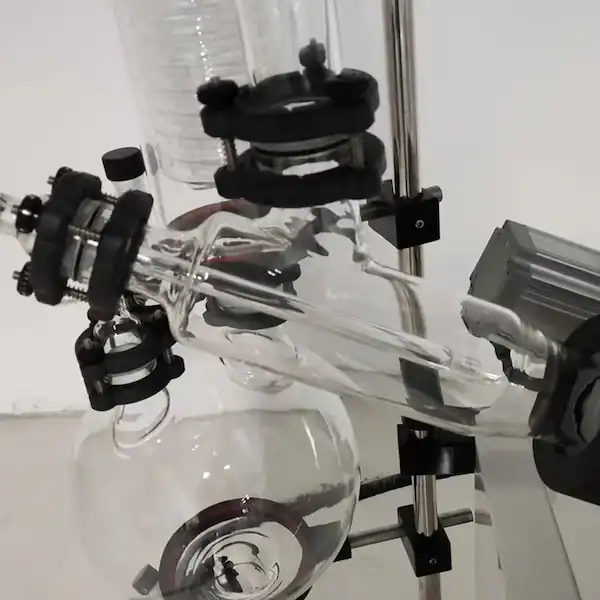
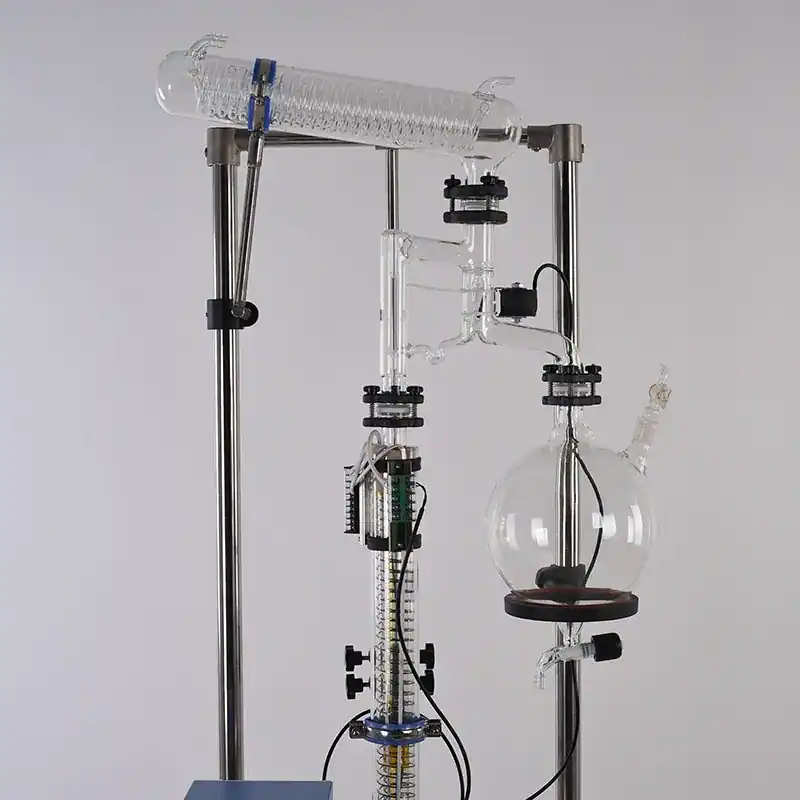
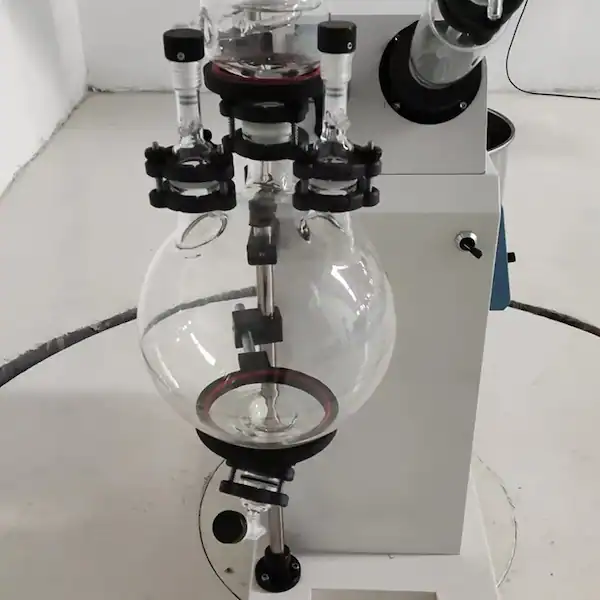




Turnkey Solutions
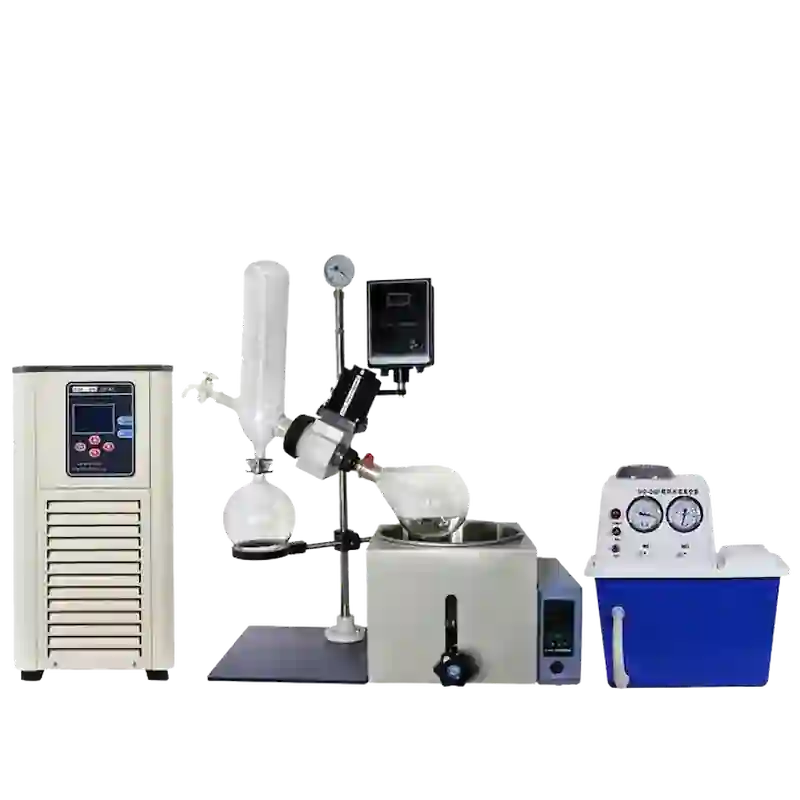
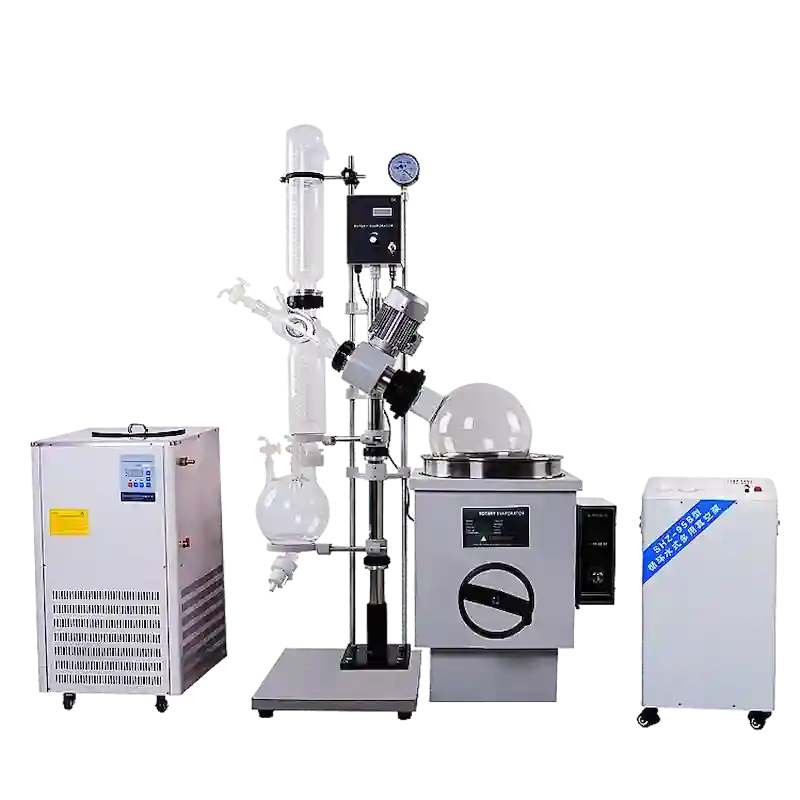



A rotary evaporator, or rotovap, is a laboratory instrument designed to efficiently and gently remove solvents from samples through evaporation. This technique is widely employed in chemistry, biochemistry, and molecular biology for concentrating solutions and processing compounds. The rotary evaporator is particularly advantageous when working with heat-sensitive materials that may decompose at higher temperatures.
The principle of a rotary evaporator, or rotary vacuum evaporator, is to operate under vacuum conditions, employing constant temperature heating and rotation at a fixed speed. This creates a large film on the bottle wall, facilitating high-efficiency evaporation based on different boiling points. The vapor generated is efficiently cooled by an advanced glass condenser and then recycled into the collection bottle, resulting in the extraction of the target solvent.
When considering a rotary evaporator purchase, it’s essential to factor in the rotary evaporator price, as it varies based on the model and features. Labonsale offers competitive rotary evaporator prices, ensuring that laboratories and industries can access top-notch equipment without compromising quality.
Structure of Rotary Evaporator
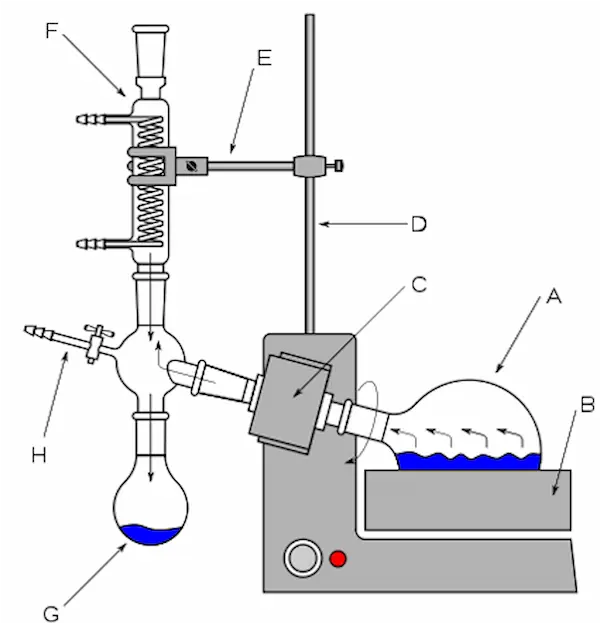
A) Round bottom flask B)Water bath C) Rotary motor F)Water condenser G) Receiving flask/collecting reservoir H) Tap connecting vacuum pump.
Reduced pressure within the apparatus lowers the boiling point of the solvent in the round bottom flask. Rotating the flask increases the liquid’s surface area, accelerating the evaporation rate. The solvent vapor moves into the cooler water condenser, condenses, and then drips into a separate receiving flask. This entire process effectively removes the solvent, leaving behind a concentrated compound in the original round bottom flask.
Why use it?
Rotary evaporation is commonly employed to remove solvents with relatively low boiling points, such as ethyl acetate (EtOAc) and n-hexane, from a sample. This method is favored for its simplicity, quick solvent removal (depending on volume and solvent type), and widespread availability in most organic laboratories. It is also more efficient than evaporation under atmospheric pressure.
However, solvents like water or dimethylformamide (DMF) with higher boiling points pose a challenge for standard rotary evaporators. To address this, a vacuum system capable of achieving sufficiently low pressure is required. In cases where water is present, it is often removed before using a rotary evaporator by employing drying agents such as magnesium sulfate (MgSO4).
Brief overview of how a rotary evaporator works
Sample Preparation: The sample to be concentrated is placed in a round-bottom flask, often with a solvent.
Evaporation: The round-bottom flask is attached to the rotary evaporator, and the system is assembled. The flask is partially immersed in a heated water bath, and the solution is gently rotated to increase the surface area for evaporation.
Vacuum System: A vacuum pump is used to reduce the pressure in the system, lowering the boiling point of the solvent and facilitating its removal at lower temperatures.
Condensation: As the solvent evaporates from the sample, it rises into the condenser, where it is cooled and condensed back into a liquid state. The condensed solvent is collected in a separate container, leaving the concentrated sample in the round-bottom flask.
Collection: The concentrated sample is then collected for further analysis or processing.
Rotary evaporators are versatile tools, and their applications extend beyond simple solvent removal. They are also used for molecular distillation, where compounds with different boiling points can be separated, and for solvent recycling, reducing waste and cost in the laboratory.
It’s important to note that safety precautions, such as proper ventilation and adherence to temperature and pressure limits, should be followed when using a rotary evaporator to ensure the well-being of the operator and the integrity of the experiment.
How To Use Rotary Evaporator
The rotary evaporator machine is relatively simple to use, but the correct procedure should be followed.
- Turn on the water bath and set it to the desired temperature.
- Ensure water is flowing into the water condenser.
- Connect the round bottom flask to the rotary evaporator (rotavap), using a clip to secure the flask in place.
- Turn on the vacuum pump, then promptly close the tap to create reduced pressure in the system.
- Activate the rotation of the round bottom flask.
- Wait briefly to observe any bumping, and then lower the round bottom flask into the water bath.
- Monitor the round bottom flask until the solvent is completely removed.
- Once the process is complete, raise the round bottom flask out of the water bath and stop the rotation.
- Turn off the vacuum pump, and carefully open the tap immediately to release the system from reduced pressure.
- The round bottom flask should now be ready to be removed from the rotary evaporator.
Go back to homepage
View more about Rotary evaporator on Wikipedia


















